Introduction: What is ICD-10 Code D50.9?
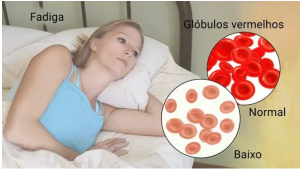
ICD-10 Code D50.9 refers to iron deficiency anaemia, unspecified. This finding is for the most part used in the clinical field to portray a condition where the body needs satisfactory iron to make haemoglobin, the protein in red platelets that passes oxygen all on through the body. In this total helper, we’ll research the significance of ICD-10 code D50.9, its ideas in clinical practice, and how clinical consideration providers can ensure precise coding for this ordinary yet troublesome condition.
As one of the most broadly perceived kinds of whiteness, iron insufficiency sickliness impacts an enormous number of people all over the planet, regularly provoking exhaustion, inadequacy, and different secondary effects. ICD-10 code D50.9 is used when the kind of absence of iron whiteness isn’t shown further. This article will dive into its significance in clinical consideration, its causes, aftereffects, assurance, and treatment decisions.
What Causes Iron Deficiency Anemia (ICD-10 Code D50.9)?

Iron deficiency anaemia is caused by a lack of iron in the body,which is major for the advancement of haemoglobin. Haemoglobin is a protein found in red platelets that is obligated for moving oxygen from the lungs to the rest of the body. Right when the body needs more iron, it can’t convey adequate sound red platelets, provoking the condition known as absence of iron sickliness.
The fundamental drivers of absence of iron shortcoming include:
Dietary Insufficiency: The most broadly perceived justification for absence of iron sickliness is an eating schedule that avoids a sufficient number of iron-rich food sources like red meat, spinach, and empowered grains.
Blood Adversity: Continuous blood mishap, every now and again as a result of gastrointestinal depleting or profound female cycle, can debilitate the body’s iron stores.
Pregnancy: Women who are pregnant require more iron due to the extended blood volume and the fostering kid’s prerequisite for iron.
Malabsorption: Conditions, for instance, celiac affliction or Crohn’s contamination can impact the body’s ability to ingest iron from food.
By understanding these causes, clinical benefits providers might even more at any point exactly break down and treat absence of iron shortcoming using ICD-10 code D50.9.
Symptoms of Iron Deficiency Anaemia

The side effects of lack of iron paleness can fluctuate from one individual to another and may go from gentle to extreme. Normal side effects include:
Exhaustion and Shortcoming: One of the most well-known side effects of lack of iron sickliness is overpowering sleepiness, which happens on the grounds that the body’s phones are not getting sufficient oxygen.
Fair Skin: A perceptible whiteness in the skin, especially around the face and within the eyelids, is normal.
Windiness: People with iron inadequacy sickliness might feel winded, even after light actual effort.
Heart Palpitations: The heart might pulsate quicker with an end goal to make up for the absence of oxygen in the circulation system.
Tipsiness or Unsteadiness: Decreased oxygen levels in the blood can cause sensations of dazedness or blacking out.
ICD-10 Code D50.9 Diagnosis and Testing

Diagnosing absence of iron paleness consistently incorporates a couple of stages, and the ICD-10 code D50.9 is basic for definite clinical charging and documentation. Here are the typical illustrative methods used:
Blood Tests: An all out blood count (CBC) can uncover a diminished number of red platelets and lower haemoglobin levels. Additional tests to check ferritin (a protein that stores iron) and serum iron levels assist with concluding whether absence of iron is the explanation.
Iron Assessments: These tests help with studying how much iron in the blood and conclude whether there is a need.
Reticulated Count: This test gauges the amount of energetic red platelets in the blood, which may be lower in people with absence of iron whiteness.
Endoscopy or Colonoscopy: If continuous blood incident is thought, (for instance, from a ulcer or gastrointestinal kicking the bucket), an expert could recommend these techniques to track down the wellspring of passing on.
By using ICD-10 code D50.9, clinical benefits specialists can record the condition unequivocally and ensure that the patient seeks legitimate treatment.
Treatment Options for Iron Deficiency Anaemia (ICD-10 Code D50.9)

The treatment for lack of iron paleness is pointed toward renewing iron stores and tending to the hidden reason for the inadequacy. The following are a portion of the essential treatment choices:
Iron Enhancements: The most widely recognised treatment for lack of iron sickliness is iron supplementation, regularly as oral iron pills. These are frequently prescribed for quite a long time to reestablish iron levels.
Dietary Changes: An eating regimen wealthy in iron can assist with working on iron levels. Food sources like lean red meats, verdant green vegetables, beans, and braced grains are incredible wellsprings of iron.
Intravenous (IV) Iron: In serious cases or when oral enhancements are not viable, intravenous iron might be regulated in a clinical setting.
Treating Basic Causes: In the event that the sickliness is because of persistent blood misfortune, (for example, from a gastrointestinal condition), treating the fundamental issue is fundamental to forestall further iron misfortune.
With opportune and viable treatment, people with iron lack weakness can recuperate and get back to ordinary well being.
Preventing Iron Deficiency Anaemia
Forestalling lack of iron sickliness includes keeping a solid eating routine, especially one wealthy in iron and other fundamental supplements. Customary clinical check-ups, especially for people at higher gamble (like pregnant ladies and those with gastrointestinal issues), can likewise help distinguish and address paleness before it becomes serious.
Iron-Rich Food sources: Eating iron-rich food sources everyday can assist with forestalling the beginning of lack of iron sickliness.
Iron Enhancements: In specific high-risk gatherings, for example, pregnant ladies or people with ongoing blood misfortune, iron enhancements might be suggested as a preventive measure.
Conclusion: Managing Iron Deficiency Anaemia with ICD-10 Code D50.9
Lack of iron pallor, as shown by ICD-10 code D50.9, is an inescapable and treatable condition. By perceiving the causes, side effects, and treatment choices for this sort of iron deficiency, medical services suppliers can successfully deal with the condition and work on understanding results. Also, precise coding and documentation guarantee legitimate charging and consistence in clinical practices.